1. Bae ON, Serfozo K, Baek SH, et al. (2013) Safety and efficacy evaluation of carnosine, an endogenous neuroprotective agent for ischemic stroke. Stroke 44(1):205-12.
2. Candelario-Jalil E, Munoz E, Fiebich BL. (2008) Detrimental effects of tropisetron on permanent ischemic stroke in the rat. BMC Neurosci 9:19
3. Chen HZ, Guo S, Li ZZ, et al. (2014) A critical role for interferon regulatory factor 9 in cerebral ischemic stroke.J Neurosci.34(36):11897-912.
4. Huang J, Kim LJ, Poisik A, Pinsky DJ, Connolly ES, Jr. (1998) Does poly-L-lysine coating of the middle cerebral artery occlusion suture improve infarct consistency in a murine model? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 7:296-301
5. Gu L, Xiong X, Zhang H, et al. (2012) Distinctive Effects of T Cell Subsets in Neuronal Injury Induced by Cocultured Splenocytes In Vitro and by In Vivo Stroke in Mice. Stroke 43:1941-1946.
6. Ishizaka S, Horie N, Satoh K, et al. (2013) Intra-arterial Cell Transplantation Provides Timing-Dependent Cell Distribution and Functional Recovery After Stroke. Stroke 44:720-726.
7. Jin R, Song Z, Yu S, et al. (2011) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke.Stroke 42(7):2033-44.
8. Khan M, Jatana M, Elango C, Paintlia AS, Singh AK, Singh I. (2006) Cerebrovascular protection by various nitric oxide donors in rats after experimental stroke. Nitric Oxide 15:114-124
9. Kleinschnitz C, Pozgajova M, Pham M, Bendszus M, Nieswandt B, Stoll G. (2007) Targeting platelets in acute experimental stroke: impact of glycoprotein Ib, VI, and IIb/IIIa blockade on infarct size, functional outcome, and intracranial bleeding. Circulation 115:2323-2330
10. Koizumi J, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T, Ooneda G. (1986) Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema, I: a new experimental model of cerebral embolism in rats in which recirculation can be introduced in the ischemic area. Jpn J Stroke 8:1-8
11. Liu S, Liu W, Ding W, Miyake M, Rosenberg GA, Liu KJ. (2006) Electron paramagnetic resonance-guided normobaric hyperoxia treatment protects the brain by maintaining penumbral oxygenation in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1274-1284
12. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84-91
13. Maysami S, Lan JQ, Minami M, Simon RP. (2008) Proliferating progenitor cells: a required cellular element for induction of ischemic tolerance in the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1104-1113
14. Pignataro G, Simon RP, Boison D. (2007a) Transgenic overexpression of adenosine kinase aggravates cell death in ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1-5
15. Pignataro G, Simon RP, Xiong ZG. (2007b) Prolonged activation of ASIC1a and the time window for neuroprotection in cerebral ischaemia. Brain 130:151-158
16. Pignataro G, Studer FE, Wilz A, Simon RP, Boison D. (2007c) Neuroprotection in ischemic mouse brain induced by stem cell-derived brain implants. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:919-927
17. Ruscher K, Kuric E, Wieloch T, et al. (2012) Levodopa Treatment Improves Functional Recovery After Experimental Stroke. Stroke 43:507-513.
18. Sakata H, et al. (2012) Minocycline-Preconditioned Neural Stem Cells Enhance Neuroprotection after Ischemic Stroke in Rats. J Neurosci. 32(10):3462–3473.
19 Schmid-Elsaesser R, Zausinger S, Hungerhuber E, Baethmann A, Reulen HJ. (1998) A critical reevaluation of the intraluminal thread model of focal cerebral ischemia: evidence of inadvertent premature reperfusion and subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats by laser-Doppler flowmetry. Stroke 29:2162-2170
20. Shah ZA, Namiranian K, Klaus J, Kibler K, Dore S. (2006) Use of an optimized transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery protocol for the mouse stroke model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 15:133-138
21. Shimamura N, Matchett G, Tsubokawa T, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. (2006a) Comparison of silicon-coated nylon suture to plain nylon suture in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J Neurosci Methods 156:161-165
22. Shimamura N, Matchett G, Yatsushige H, Calvert JW, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. (2006b) Inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 ameliorates focal cerebral ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Stroke 37:1902-1909
23. Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Cahill J, Zhang JH. (2006) Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 143:965-974
24. Tsubokawa T, Jadhav V, Solaroglu I, Shiokawa Y, Konishi Y, Zhang JH. (2007) Lecithinized superoxide dismutase improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats. Stroke 38:1057-1062
25. Tsubokawa T, Solaroglu I, Yatsushige H, Cahill J, Yata K, Zhang JH. (2006a) Cathepsin and calpain inhibitor E64d attenuates matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 37:1888-1894
26. Tsubokawa T, Yamaguchi-Okada M, Calvert JW, Solaroglu I, Shimamura N, Yata K, Zhang JH. (2006b) Neurovascular and neuronal protection by E64d after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci Res 84:832-840
27. Tsuchiya D, Hong S, Kayama T, Panter SS, Weinstein PR. (2003) Effect of suture size and carotid clip application upon blood flow and infarct volume after permanent and temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 970:131-139
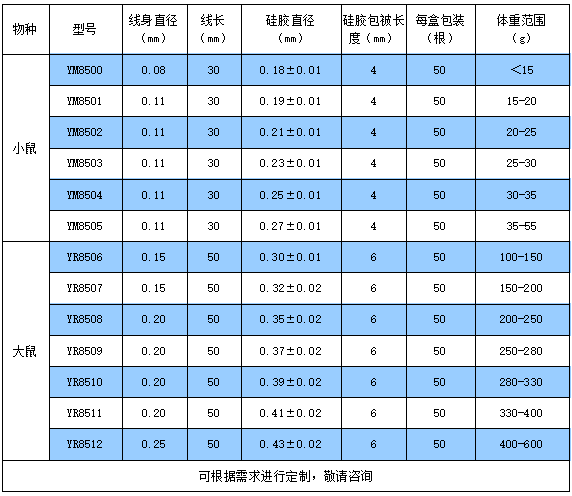
MCAO模型脑缺血手术中常用的手术器械,可供参考:
手术显微镜(小鼠使用,大鼠可以不用)
冷光源
动物体温维持仪
剃毛器
手术剪 12cm 直
眼科镊 10cm 弯 2把
显微镊 11cm 或者 14cm 弯
显微剪 12cm 直(剪血管使用)
切线剪
大小鼠撑开器 8cm
血管夹 4cm
动脉夹 1.5cm 2个
持针钳
缝合针(或带针缝合线)
缝合线
还可以根据需求,选择小动物气体麻醉机:
小动物气体麻醉机

动物保温系统
动物体温维持仪(电热型)对手术中的动物和术后恢复的动物进行保温,并可进行动物体温测量。