小动物断头处死器,实验动物断头器
企业档案
会员类型:会员

已获得易推广信誉 等级评定
(0 -40)基础信誉积累,可浏览访问
(41-90)良好信誉积累,可接洽商谈
(91+ )优质信誉积累,可持续信赖
易推广会员:5年
最后认证时间:
注册号:**** 【已认证】
法人代表: 【已认证】
企业类型:个体商户 【已认证】
注册资金:人民币***万 【已认证】
产品数:1550
参观次数:836019
详细内容
老鼠断头器的主要特点:
· 迅速将大鼠、小鼠或小动物斩;
· 刀刃是手磨不锈钢,中间有一个边长1.75英寸开口;
· 无需拆卸,表面易于清洗;
· 底部安放在操控台上,压杆容易操控

您还可以选择二氧化碳安乐处死箱,对实验动物进行安乐处死(推荐使用)
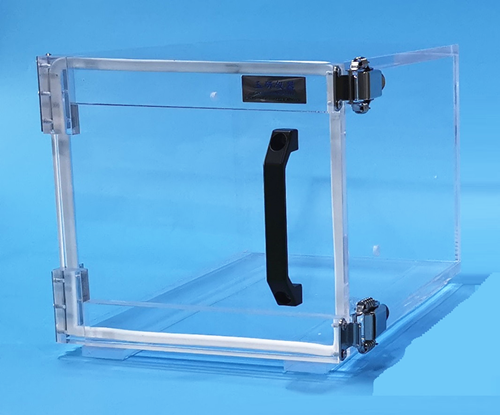
手动型安乐处死箱
· 密闭性好,结实耐用;
· 材料透明,方便观察;
· 尺寸可以订做,也可以进行其他特别的改进和设计。

主要规格型号:
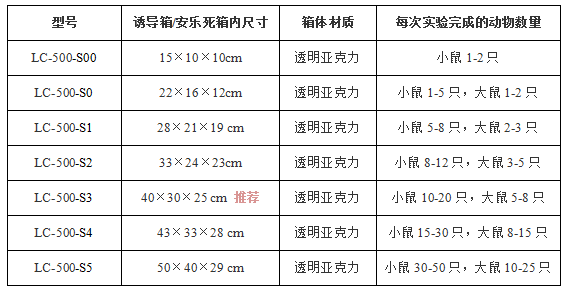
自动型小动物安乐处死系统

CL-1000型小动物安乐处死系统采用自动化控制的二氧化碳缺氧致死的方式,控制和增加箱体内二氧化碳的浓度,并在达到一定的浓度后,自动切断气源,维持一定的诱导时间,在没有惊扰、轻微的痛苦中,对动物进行快速的诱导死亡。
CL-1000型小动物安乐处死系统与常规型手控流量控制式安乐处死箱相比较,有明显的优势:
使用便捷:自动化程度高,一键式完成操作;
省事省力:系统可自动进行充气、维持和清除废气的作业;
参数可调:流速、通气时间、维持时间、废气清洗时间可调可控;
使用更安全:自动清除箱体内的大量二氧化碳和废气,确保实验室的安全,可连续进行多批次的实验操作;
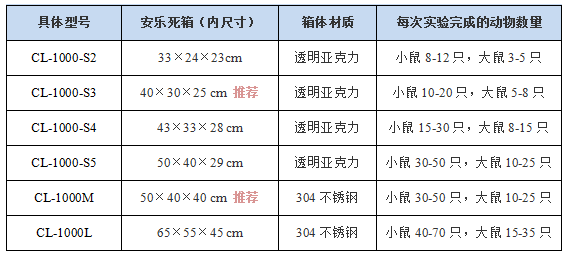
一体式小动物安乐处死系统

型号:CL-2000
主要特点:
· 设备为一体式设计,可隔放在实验台上使用
· 系统可预设程序,自动往二氧化碳处死箱内通入设定量的二氧化碳
· 多种参数可进行设置:流速、通气时间、维持时间、废气冲洗时间,紫外杀菌时间
· 设置参数后,可一键式操作即可完成动物麻醉、二氧化碳处死、废气清除的整个操作,过程中无需有人值守
· 二氧化碳气体通入流速:0-50L/min,数字化显示,调控精度为0.01L/min
· 设备具有CO2传感器,能实时检测箱体内CO2浓度,并可调节和控制箱体内CO2的浓度
· 全触摸屏操作,人性化界面设计,显示屏上可同屏显示多种运行状态
定制型小动物安乐处死箱
无二氧化碳废气泄露,适合SPF屏障实验室
型号:LC-800-S1
部分参考文献:
1. Li J, Zhang Z, Qiu J, Huang X. 8-Methoxypsoralen has Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Roles in Osteoarthritis Through SIRT1/NF-κB Pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2021-September-06 2021;12.
2. Xu L, Wang S, Shen H, et al. Analgesic and toxic effects of venenum bufonis and its constituent compound cinobufagin: A comparative study. Neurotoxicology and Teratology. 2019;73:49-53.
3. Tian J, Zhou D, Xiang L, et al. Calycosin represses AIM2 inflammasome-mediated inflammation and pyroptosis to attenuate monosodium urate-induced gouty arthritis through NF-κB and p62-Keap1 pathways. Drug Development Research. 2022/11/01 2022;83(7):1654-1672.
4. Li Y, Yu H, Lv M, Li Q, Zou K, Lv S. Combination therapy with budesonide and N-acetylcysteine ameliorates LPS-induced ALI by attenuating neutrophil recruitment through the miR-196b-5p/Socs3 molecular axis. BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 2022;22(1):388.
5. Cui Q, Zhang D, Kong D, et al. Co-transplantation with adipose-derived cells to improve parathyroid transplantation in a mice model. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 2020;11(1):1-14.
6. Hu Q, Gao M, Zhang D, et al. De novo assembly and transcriptome characterization: Novel insights into the mechanisms of primary ovarian cancer in Microtus fortis. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2022;25(2):1-9.
7. Hu C-B, Jiang H, Yang Y, et al. DL-3-n-butylphthalide alleviates motor disturbance by suppressing ferroptosis in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regeneration Research. 2023;18(1):194.
8. Guo G, Sun L, Yang L, Xu H. IDO1 depletion induces an anti-inflammatory response in macrophages in mice with chronic viral myocarditis. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(20):2598-2613.
9. Pan W, Xu X, Wang Y, Song X. Interleukin-35 reduces inflammation in acute lung injury through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2020;19(3):1695-1700.
10. Zhao C, Jiang Q, Chen L, Chen W. LncRNA LINC01535 promotes colorectal cancer development and chemoresistance by sponging miR-761. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2021;22(1):1-10.
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
TEL : , 18502129044
QQ : 2113136797
Mail: yuyan0317@126.com
敬请来电咨询!










